Images
Researchers working with flies at IRB Barcelona describe that the concentration of some small intracellular organelles determines the branching capacity of tracheal cells.
Tracheal cells are analogous to the cells that form blood vessels in the human body. The inhibition or stimulation of new blood vessels has implications in cancer and in tissue regeneration.
Published today in Current Biology, a study by Sofia J. Araújo, associate researcher at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona), reveals that the number of centrosomes—small intracellular structures—in cells determines the final shape that cells adopt and their function.
The effects of variations in the number of centrosomes are studied mainly in dividing cells because of the key function of centrosomes in this process and their correlation with cancer when defects are present. Araújo’s team, which works in Jordi Casanova’s Development and Morphogenesis in Drosophila Lab, has now addressed the influence of variations in centrosome number on cells that have already divided and differentiated. They demonstrate that centrosomes are also determinant organelles in cells that have already left the cell-division cycle.
The greater the number of centrosomes, the greater the branching in the trachea
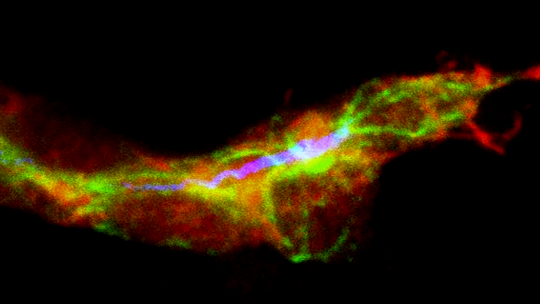
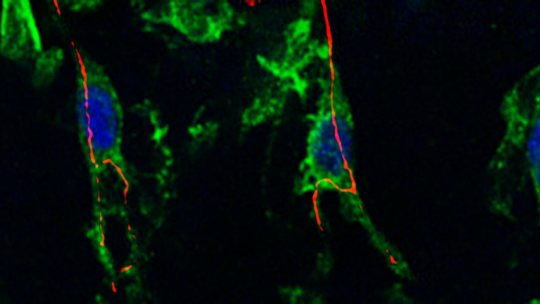
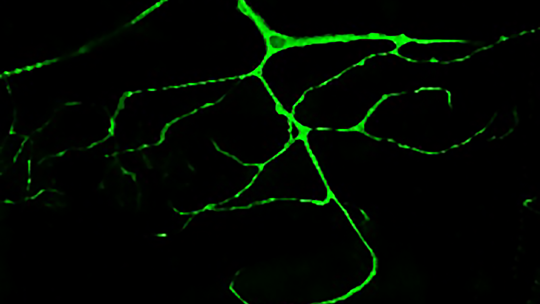
The scientists have studied centrosomes in the tracheal cells of the fly Drosophila melanogaster. In the article, they demonstrate that cells that hold more than two centrosomes form more branches (a single cell is like a small tree with many branches). In contrast, those that have two (the usual number) form standard branches, while those that have none show practically no branching.
This finding indicates variations in the number of centrosomes affect the morphology of tracheal cells. In addition, the study describes that the number of centrosomes is related to the first developmental stages of these structures in the fly respiratory system. “Through our work, we have been able to modify the capacity of these cells to branch in function of the number of centrosomes that we introduce. This finding may have biomedical implications,” says Araújo.
Of biomedical interest
Tracheal cells are homologous structures to the cells that form the delicate blood vessels of the human body. The formation of new vessels (from those already existing (angiogenesis) or new ones (neovascularisation) has two implications in human health. On the one hand, medical practice seeks how to inhibit pathological angiogenesis, for example in cancer, when tumour cells generate more blood vessels to facilitate access to more oxygen and nutrients, thus ensuring their growth. On the other hand, and in contrast, it may be of interest to stimulate the formation of new vessels, for example for wound healing or in regenerative processes.
Beyond the widely studied effects of centrosomes on cell division, the work by Araújo provides new information on the function of these organelles and their possible contribution to disease in differentiated cells.
Reference article:
Centrosome amplification increases single-cell branching in post-mitotic cells
Delia Ricolo, Myrto Deligiannaki, Jordi Casanova and Sofia J. Araújo
Current Biology (2016) doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.08.020
About IRB Barcelona
The Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) pursues a society free of disease. To this end, it conducts multidisciplinary research of excellence to cure cancer and other diseases linked to ageing. It establishes technology transfer agreements with the pharmaceutical industry and major hospitals to bring research results closer to society, and organises a range of science outreach activities to engage the public in an open dialogue. IRB Barcelona is an international centre that hosts 400 researchers and more than 30 nationalities. Recognised as a Severo Ochoa Centre of Excellence since 2011, IRB Barcelona is a CERCA centre and member of the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (BIST).