Images
Participants




Contact

Diseases that stem from or are affected by defective amino acid transport, such as cancer, cystic fibrosis or neurodegenerative conditions, may benefit from advances in this field.
The work, a collaboration between the Amino Acid Transporters and Disease laboratory at IRB Barcelona and the Ballester group at ICIQ, has been published in the journal CHEM.
The collaboration has taken place under the BIST Ignite project CALIX4TRANS.
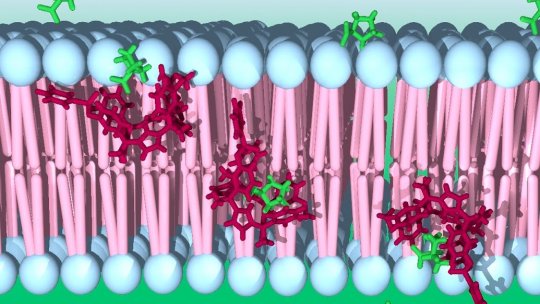
The transport of amino acids and other molecules across the cell membrane plays a crucial role in cell metabolism and, therefore, in human health. Current research hints that cancer, cystic fibrosis, aminoacidurias and neurodegenerative diseases may stem from or be affected by missing or defective amino acid transport at the cell membrane. Now, researchers from ICIQ’s Ballester group and IRBBarcelona's Amino Acid Transporters and Disease laboratory, led by Manuel Palacín, have published a paper in Chem showing how a synthetic carrier calix[4]pyrrole cavitand can transport amino acids across liposomes and cell membranes bringing future therapies a step closer.
Thanks to the BIST Ignite project CALIX4TRANS, the scientists have studied the properties of a calix[4]pyrrole cavitand (a container-shaped molecule) in the transport of the amino acid Proline through cell and liposomal membranes. “The BIST Ignite project has allowed us to combine the fundamental research done in our lab focused on making molecules and studying their interactions with the more applied research done in Palacin’s group in the area of amino acid transporters and diseases. In my opinion, applied research must go hand in hand with basic research for a better understanding and advancement of science. In this case applying a synthetic carrier as therapeutic tool for Proline-dependent diseases like some cancers and inherited hyperprolinemias” explains Gemma Aragay, scientific coordinator of ICIQ’s Pau Ballester group.
The scientists made liposomes in which the cavitand was embedded in the membranes. They observed a 30-fold increase in L-Proline transport activity when compared with the passive diffusion of the amino acid to the interior of “regular” liposomes, as well as the selectivity of the cavitand for L-Proline over other amino acids. “L-Proline is a suitable guest for the Calix[4]pyrrole cavitand because of the complementarity between the cavity’s size, shape and functional groups with those of the amino acid,” explains Aragay.
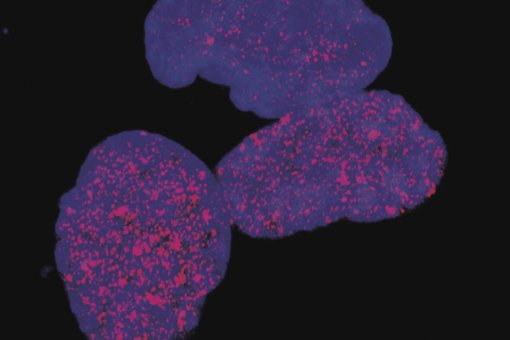
To study the impact of the cavitand on Proline transport in living cells, the scientists incubated cultured HeLa cells with synthetic vesicles infused with Calix[4]pyrrole in order to incorporate the cavitand in the cell membranes. The results obtained reveal that the presence of the cavitand increases the diffusion of proline at high extracellular amino acid concentrations – although it is a moderate increase when compared with the transport carried out by the cell proteins.
However promising the results are, “we need to further study the molecular structure of the cavitand-amino acid complex to increase the transport activity if we want to apply Calix[4]pyrroles as therapeutic tools,” explains Pau Ballester, ICIQ group leader and ICREA professor.
“With this work, we hope to drive the development of artificial carriers to efficiently treat diseases of amino acid metabolism,” concludes Manuel Palacín, Head of the Amino Acid Transporters and Disease lab at IRB Barcelona, group leader at CIBER of Rare Diseases, and Professor at the University of Barcelona.
Reference article:
Facilitated Diffusion of Proline across Membranes of Liposomes and Living Cells by a Calix[4]pyrrole Cavitand
Luis Martínez-Crespo, Jia Liang Sun-Wang, Andres Felipe Sierra, Gemma Aragay, Ekaitz Errasti-Murugarren, Paola Bartoccioni, Manuel Palacín, P. Ballester
Chem, 2020 (DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2020.08.018).
About IRB Barcelona
The Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) pursues a society free of disease. To this end, it conducts multidisciplinary research of excellence to cure cancer and other diseases linked to ageing. It establishes technology transfer agreements with the pharmaceutical industry and major hospitals to bring research results closer to society, and organises a range of science outreach activities to engage the public in an open dialogue. IRB Barcelona is an international centre that hosts 400 researchers and more than 30 nationalities. Recognised as a Severo Ochoa Centre of Excellence since 2011, IRB Barcelona is a CERCA centre and member of the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology (BIST).